Integumentary System of Human Body - Definition and Information
Referring to the envelope of an ovule in Botany, it forms an outer natural coat or covering among animals, such as the skin enclosing all the organs of the body or a membrane around a single organ. Comprising of the skin and its appendages, this organ system in humans serves to protect the body against different kinds of damages, including abrasion from outside and the loss of water.
The appendages of the integumentary system are comprised of hair, nails, hooves, scales and feathers. However, the appendages, found in humans, include nails and hair, while hooves, scales and feathers are present in the nonhuman animals.
Among a variety of functions, performed by this organ system, there include cushioning, waterproofing and protecting the deeper tissues in the body, excretion of waste products, and playing a role in the regulation of internal temperature. Likewise, it also serves as an attachment site for the sensory receptors that are concerned with the detection of pain, pressure, temperature and sensation.
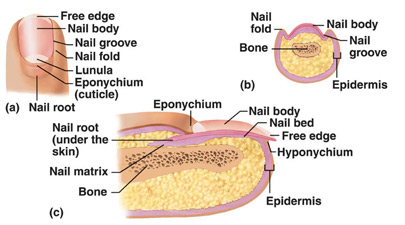
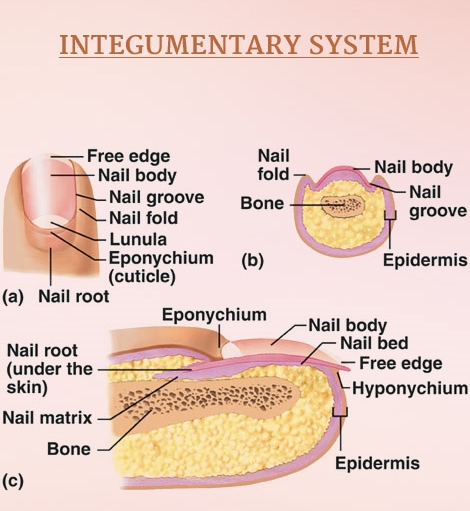
Still another function of the integumentary system is to assist vitamin D synthesis in most of the terrestrial vertebrates that have significant exposure to sunlight. Talking of functionality of the nails, they render hardness and beauty to the tips of the fingers and toes.
The hair, besides adding to the charm of your personality, contributes to the protection of your brain and skull as the impact of hard stroke on the head gets significantly diminished. On the basis of these particular facts, one can be sure to say that the human integumentary system is of immense importance as it accomplishes a variety of indispensable tasks in the body.
The medical conditions affecting your skin, nails, hair and associated structures are usually grouped as the integumentary system diseases. However, the organs of this system also get affected by and reveal the symptoms of the disorders related with other organs and organ systems in the body. In this way, the diagnosis of certain abnormalities becomes quite easier for your healthcare provider.
For example, in case of damages to the liver, the skin turns a bit yellowish due to accumulation of the bile pigments in the blood circulating through the skin, thus revealing the symptoms of jaundice or hepatitis. In another instance, the impaired circulatory function or respiratory function is indicated by the bluish discoloration of the skin that results from the inadequate oxygenation of the circulatory fluid blood.
Similarly, the rashes and lesions in the skin are said to be symptomatic of the problematic conditions elsewhere in the body. In the allergic reactions, histamine is released into the tissues, which causes swelling as well as reddening of the skin. When there is excessive production of keratin, owing to the deficiency of vitamin A, a characteristic sand paper texture is assumed by the skin.
Other related disorders of the integumentary system include shingles, rosacea, psoriasis, impetigo and dermatitis. The treatment is carried out either through oral administration of medication or by the topical application of drugs. In any case, the victims are advised to consult their healthcare provider as soon as possible for the sake of easier and quicker remedy.
Informative Articles About "Human Integumentary System"
Integumentary System Parts
Skin, nails and hair are the major human integumentary system organs, where ...
Integumentary System Functions
Just like any other organ system in your body, the integumentary...
Integumentary System Facts
Comprising of the body hair, nails and skin, the integumentary...
Integumentary System Diseases
Any medical condition associated with the skin, ...